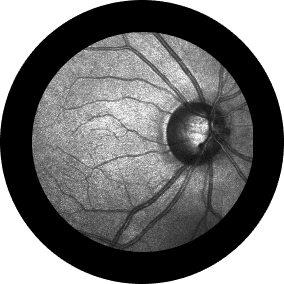
Diagnosis
The retina is an extension of the brain. It forms the interior lining of the eye and contains millions of light-sensitive nerve endings. The vitreous is a clear, gel-like substance that fills the cavity between the lens and the retina.
A large variety of conditions can affect
the vitreous and retina that lie on the back part of the eye that is not readily visible, such as macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, retinal vascular occlusions, retinal detachments or tears, macular holes, uveitis, eye cancer and inherited retinal diseases.
At Retina Wellness and Surgery, we believe that early detection optimizes patient outcomes and we take a holistic approach to patient care taking into account patients’ fear of going blind, inability to read or drive. In addition to providing our patients with the highest quality eye care, we offer the latest in imaging technology to provide detailed information about the structure of the eye to help guide diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms and Causes

Flashes/Floaters/Shadows
Symptoms
Sudden onset of floaters, cobwebs, blurred vision, flashes of light or shadows especially in dim environment or with eye movement.
Differential Diagnosis
Vitreous Hemorrhage: bleeding in the back of the eye from posterior vitreous detachment, retinal tear/detachment or diabetes, etc.
Retinal Tear: As the vitreous gel degenerates, it pulls on the retina and can tear the retina
Retinal Detachment: As the retina gets torn without treatment, retina can detach from the wall of the eye
Uveitis: inflammation inside the eye
Migraine
When to “book a consultation” immediately:
- You have a sudden onset of many new, large or dark floaters
- You have a sudden onset of flashes that persist or increase in frequency
- You have a decrease in vision
- You see a shadow or part of your vision missing

Macular Degeneration
Symptoms
Gradual loss of the central vision or no symptoms
Types
Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration
As the center of the retina ages, waste deposits called drusen accumulate damaging the retina causing blurred vision. Risk factors include age, smoking, family history, poor diet, high cholesterol, cardiovascular diseases, etc.
Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration
As the waste deposits continue to accumulate, further damage is done to the retina causing the retina to bleed or leak fluid.
When to “book a consultation” immediately:
- Sudden onset of central visual loss
- Sudden onset of distortion in vision
- Sudden onset of flashes of light in the central visual field

Diabetic Retinopathy
Symptoms
Blurred vision, floaters, distortion of vision
Major Causes
Major causes of vision loss from diabetes damaging retinal blood vessels:
Diabetic Macular Edema: swelling of the retina from abnormal leakage of fluid or blood
Vitreous hemorrhage/Tractional retinal detachment: As blood vessels continue to be damaged, they are fragile and can bleed easily. These abnormal blood vessels can also pull on the retina and detach the retina
Retina Ischemia: These damaged blood vessels cannot supply enough blood to the retina further damaging the retina
When to “book a consultation” immediately:
- You have a sudden onset of many new, large or dark floaters
- You have a decrease in vision in the central or peripheral part of the visual field
- You see a shadow or part of your vision missing

Retinal Vascular Occlusions
Symptoms
Blurred vision, floaters, distortion of vision
Types
Central/Branch Retinal Artery Occlusion: blockage of either the central retinal artery or a branch of the retinal artery causing starvation of blood to the entire retina or part of the retina.
Central/Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion: blockage of either the central retinal vein or a branch of the retinal vein causing backup of blood to the retina.
Causes
Diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, etc.
When to “book a consultation” immediately:
- You have a sudden decrease in vision in the entirety or peripheral part of the visual field in one eye.
- You have a sudden onset of blurred vision especially associated with headaches, tenderness on the side of the head, pain or discomfort of the jaw when chewing.

Epiretinal Membrane/Macular Hole
Symptoms
Decreased vision, distorted vision, or no symptoms
Types
Epiretinal Membrane:
Scar tissues forming on the surface of the retina causing wrinkling of the retina and vision distortion as a result of normal aging, diabetes, inflammation, retinal tears, or prior eye surgeries, etc.
Macular Hole:
As vitreous gel ages and degenerates, the gel can pull on the central retina causing a hole in the very center of the retina.
When to “book a consultation” immediately:
- Sudden onset of central visual loss
- Sudden onset of distortion in vision
- Sudden onset of flashes of light in the central visual field
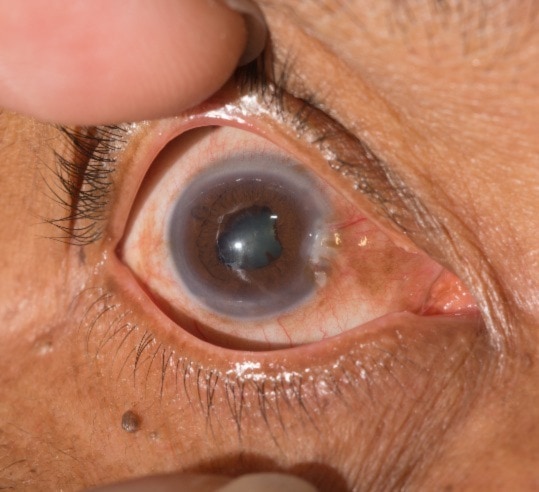
Uveitis
Symptoms
Pain, redness, light sensitivity, decreased vision, vision distortion, or floaters
What is uveitis?
Uveitis is a collection of inflammatory diseases of the uveal tract, which is the middle layer of the eye wall located between the white sclera and the inner retina. It consists mostly of blood vessels that provide nourishment for the rest of the eye.
What is uveitis?
Uveitis is a collection of inflammatory diseases of the uveal tract, which is the middle layer of the eye wall located between the white sclera and the inner retina. It consists mostly of blood vessels that provide nourishment for the rest of the eye.
Causes of uveitis
Most cases of uveitis are caused by infectious or autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, Crohn disease, etc. Trauma, certain medications and even certain cancers may cause uveitis. In many situations, a specific cause cannot be found and it is called “idiopathic” uveitis.
When to “book a consultation” immediately:
- Sudden onset of blurred vision
- Sudden onset of floaters
- Sudden onset of distortion in vision
- Sudden onset of redness or eye pain